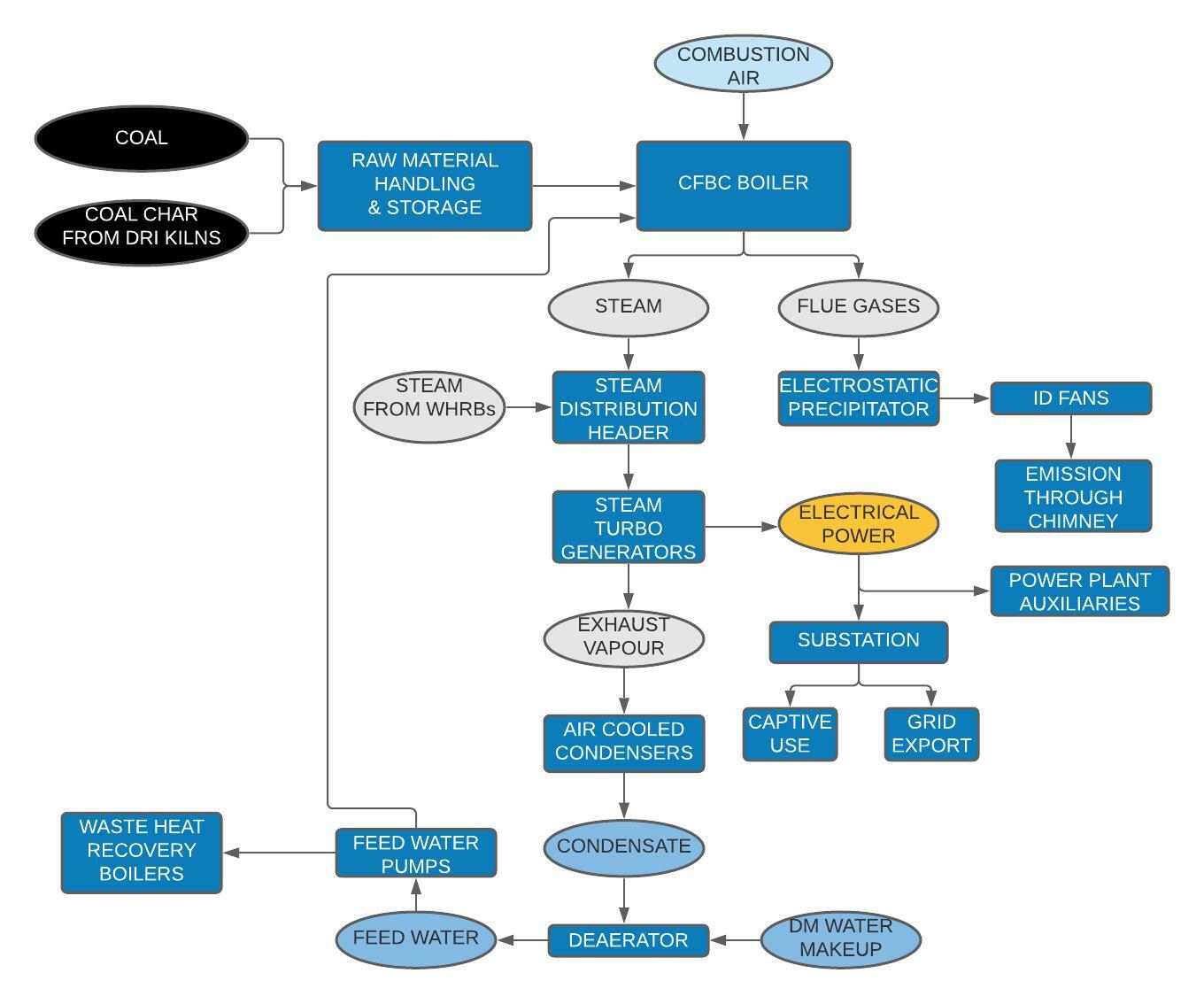
The Captive Coal Power Plant (CPP) was commissioned to meet the existing as well as the future electricity requirement of the ISP production units. The CPP has two 30 MW steam turbo generators, air cooled condensers, 210 T/hr Circulating Fluidized Bed Combustion (CFBC) boiler and two 36 T/hr Waste Heat Recovery Boilers (WHRB) in a flue gas circuit of DRI Kilns. Auxiliaries include coal and char handling system, ash/fly ash handling system, water treatment plant, water cooling system, service & instrument air compressors, power distribution system, automation with distributed control system (DCS) and a 132/11 KV substation.
Process
Coal and char are first prepared to a suitable size and transferred separately to their designated storage silos in the CFBC boiler. The bed material is also transferred to its own storage silo with a pneumatic handling system.
During the initial start-up, the CFBC boiler undergoes a thorough inspection to ascertain the condition of the refractory and a hydraulic test is conducted to identify any leaks if present. The feed water pumps then fill the boiler with water to about 50% - 60% of the steam drum level. The start-up vent valve is kept open before firing. The boiler fans are then started and fired with HSD oil to gradually increase the temperature. Once the required bed temperature is reached, the coal feeders minimum coal feeding. The boiler pressure and temperature are increased in a controlled manner. The boiler drum level, furnace drafts and combustion air are constantly monitored and manually controlled during start-up.
Once the steam temperature and pressure reaches 80% of the rated values, the main steam stop valve is slowly opened to let steam flow up to the main steam header and then drained to heat all steam headers and lines. During the operation of the DRI Kilns, flue gases pass through the WHRBs for steam generation. This steam also flows up to the main steam header.
Prior to starting, the steam turbo generators are thoroughly inspected, auxiliary cooling water pumps and lubrication oil pumps are started and turbines are kept in barring gear. The turbine steam line is charged up to the turbine drain point for slow heating the steam lines. The auxiliary steam header is charged for gland sealing and vacuum pulling. The air cooled condensers, condensate extraction pumps and ejectors are operated to start vacuum pulling. Once the rated vacuum inlet steam parameters are achieved, steam is injected into the turbine for rolling. After reaching the rated speed, the generator is excited to build voltage and synchronized with the grid. Power flow is steadily increased and after reaching 50% power generation, the HP and LP heaters are kept in operation.
Once there is load increase on the turbo generators, the start-up vent valve is closed. The boiler drum level control, furnace draft control, combustion control, and steam temperature controls are shifted to automatic control mode and monitored closely. Ash recirculation system, electro static precipitators and ash/fly ash handling system are kept running after stabilization the boiler.
Captive Coal Power Plant - Process Flow Chart